For years, attempts to build “emotion-detecting machines” carried a heavy dose of hope, but often underwhelmed. Early emotion-AI systems primarily focused on single signals (like facial expressions or voice tone), and tried to guess a person’s inner emotional state. But, we all know that doesn’t work.
Human emotion is messy. A smile doesn’t always mean happiness. A neutral face doesn’t always mean neutrality. Context matters: culture, personal expression style, environment, and even recent events shape how people show emotion. That mismatch made early emotion recognition hit-or-miss.
As sceptics liked to (and still do) point out: treating a fleeting facial expression as “anger,” “sadness,” or “joy” is overly simplistic. Reliability was low, bias was rampant, and consensus among experts was thin. Many emotion-detection tools ended up generating more questions than actionable insights. Kind of like the polygraph test that sometimes mistook heavy breathing and a fast heartbeat as lying when it could have simply been stress or anxiety.
In short: emotion AI was more speculative than dependable.
The 2026 Shift: Why This Time It’s Different
The big change: by 2026, emotion AI is no longer single-signal, it’s multimodal. That means systems simultaneously analyze facial micro-expressions, vocal tone, spoken/written words, context (past interactions, conversational history), and, with consent, physiological signals (e.g. heart rate, skin conductance).
Combining multiple signals helps reduce errors and false positives. It provides context. A change in voice tone might mean stress or just background noise. Facial tension might mean anger or concentration. But when both signals (and context) point toward frustration, the system gains confidence.
This richer, multimodal approach dramatically improves reliability making emotion detection far more practical for real-world applications.
Edge Processing + Privacy-first Architecture
By 2026, many emotion-AI systems process data on-device (“edge AI”) rather than sending everything to the cloud. That reduces latency–which is critical for real-time responsiveness (e.g. in live customer interactions). It also helps safeguard sensitive data: raw audio, video, or biometric signals never need to leave the user’s device unless consented. This dual advantage–speed and data minimization– helps overcome two big barriers that stalled early promise: practicality and privacy risk.
Is your business
AI-prepared?
Smarter Models: Working Our Way to Interpretation
Emotion isn’t just a momentary expression. It’s a story. By 2026, many solutions pair emotion-recognition modules with large language models (LLMs) or context-aware AI.
Imagine: an AI reviews a customer support call transcript, picks up on tone, pauses, word choices, and historical data, then flags that the customer is frustrated, recommends empathy, or even suggests a small discount to calm things down. Emotion becomes actionable intelligence.
The Market: It’s Already Big And Growing Rapidly
Emotion AI isn’t just a research novelty anymore. The market is real, growing fast, and broadly adopted.
- According to a report by Grand View Research, the global emotion AI market was already estimated at USD 2.14 billion in 2024 and is forecast to grow to ~USD 13.4 billion by 2033 (CAGR ≈ 22.9%) as demand rises across industries.
- Another source estimates that deployment in 2024 heavily leans toward the U.S. and other developed markets, with North America holding a substantial share of adoption.
- A third report suggests that as companies embrace AI-powered customer experiences, interaction monitoring and emotion analytics are becoming core to customer experience (CX), marketing, and digital-service stacks by 2025.
Where Emotion AI Makes Real Impact
By 2026, emotion AI will move past prototypes and land in business-critical roles. Some of the highest-impact use cases:
Marketing & Creative Optimization
Advertisers and creative teams will no longer rely solely on click-throughs or A/B tests. Emotion AI offers a deeper metric: emotional resonance.
Imagine showing several ad creatives to a focus group while emotion AI measures real-time emotional reactions. Instead of guessing which version “feels right,” you pick the one that actually makes viewers smile, frown, or react. This improves ad effectiveness, creative spend ROI, and long-term brand resonance.
Customer Service & CX Enhancement
Customer support centers in 2026 will likely have emotion-aware dashboards. AI agents will listen for frustration, anger, or confusion and prompt human agents with empathy guidelines, escalation triggers, or discount offers. It’s not about surveillance. It’s about responsiveness. Identifying emotional signals early can improve satisfaction, reduce churn, and turn unhappy customers into loyal advocates.
E-commerce & Retail: Personalization at Emotion Speed
Online shoppers don’t just respond to what they see, they respond to how they feel. Emotion AI gives retailers a new way to personalize the journey. For example: If a customer browses certain products with hesitation or confusion (detected via webcam or voice tone), the site could surface contextual help, upsell gently, or offer relevant suggestions, improving conversion while feeling human.
Automotive & Safety: Real-Time Monitoring
Automotive applications will benefit strongly. Emotion and attention detection can spot drowsiness, distraction, stress, or irritation — and trigger safety alerts or adaptive assistance. In 2026, many safety systems may include “emotional awareness” as a standard feature.
Healthcare, Telemedicine & Mental Well-Being
Emotion AI will likely make inroads into telehealth and mental-health apps, offering early detection of stress, anxiety, or depressive states. With proper consent and governance, this could support better patient monitoring, early intervention, and personalized care. But Let’s Be Clear: Emotion AI Isn’t Magic (And It Shouldn’t Be Treated Like It)
Reliability Still Varies & Bias Remains a Major Concern
Even today, research continues to highlight serious challenges with automatic facial-expression recognition (FER). A 2024 study showed that, even under ideal conditions, many FER models lacked sufficient inter-rater reliability — meaning human observers often disagreed on the “correct” emotion label before the AI even weighed in.
Ethical & Privacy Risks Are Real and Growing
Because emotion detection often relies on sensitive signals (face, voice, biometrics), it raises privacy and consent issues. Without proper transparency and controls, emotion AI can feel intrusive — especially if users don’t know they’re being “read.” There’s also a risk of misuse — e.g. in hiring, surveillance, or persuasion — especially if databases and models are biased or opaque.
Regulation & Governance Will Be Critical
By 2026, many regulators around the world (especially in the U.S., EU, and other privacy-forward jurisdictions) are expected to treat emotional data as sensitive biometric datasubject to strict consent, usage, and retention rules. Organizations that deploy emotion AI without robust governance, transparent user consent flows, and ethical oversight risk reputational, legal, and compliance problems.
A 2026-Ready Roadmap for Brands, Agencies, and Product Teams
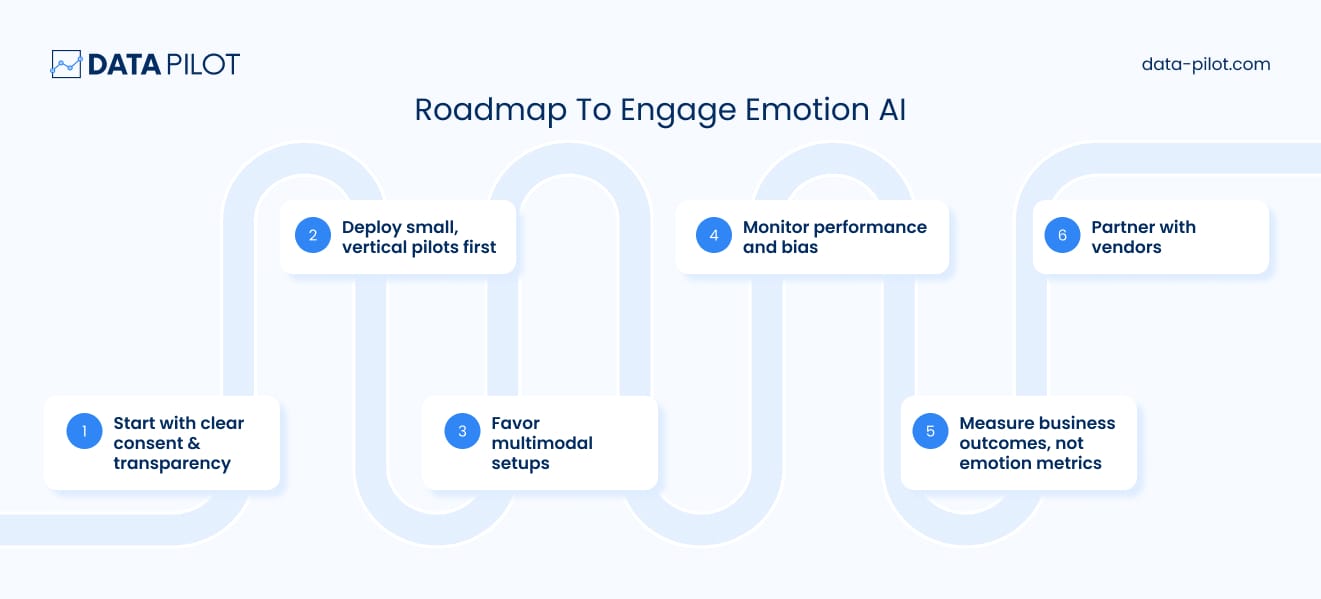
Here’s how to engage with emotion AI smartly:
1) Start with clear consent & transparency. Always inform users (or customers) when emotion data is being collected. Tell them what is collected, how it will be used, and how long it will be stored. Give them control (opt-in, opt-out, deletion).
2) Deploy small, vertical pilots first. Use emotion AI in narrow, low-risk contexts (e.g. ad testing, optional CX enhancements) rather than high-stakes decisions (hiring, credit, law).
3) Favor multimodal setups over single-signal tools. Combine facial + voice + context + optionally consented biometrics to improve reliability.
4) Monitor performance and bias. Use diverse datasets. Regularly audit results for demographic fairness and error rates.
5) Measure business outcomes, not just “emotion metrics.” Track how emotion signals correlate with real KPIs: conversion lift, retention, customer satisfaction, reduced churn, or safety improvements.
6) Partner with vendors offering transparency, compliance, and ethical guardrails. Avoid “black-box” vendors. Look for those committed to explainability, privacy-first design, and ethical AI practices, like Data Pilot.
Emotion AI in 2026: A New Layer of Understanding, If We Use It Wisely
Emotion AI is no longer a futuristic dream. By 2026, it will be a practical, widely adopted layer in customer experience, marketing, automotive safety, healthcare, and more. If we build it right — with consent, transparency, fairness, and business use in mind emotion AI won’t replace human empathy. It will simply help us understand better, respond faster, and build deeper connections.
Used well, it becomes a powerful tool for human-centered technology, customer-first experiences, and smarter decision making.
Used carelessly, it risks becoming intrusive, biased, and unfair.
The choice, as always, is ours.